Batteries vs pumped hydro – are they sustainable?
A sustainable grid needs sustainable energy sources. While there’s no doubt that it makes sense to store renewable energy, whether in batteries or in a pumped hydro scheme, just how sustainable are these technologies?

As we move rapidly towards ever-greater levels of wind and solar power in the network, increasing quantities of storage are needed to smooth intermittency and ensure secure supply. Pumped hydro energy storage and batteries are likely to do much of the heavy lifting in storing renewable energy and dispatching it when power demand exceeds availability or when the price is right.
We’ve previously compared the two technologies in terms of their costs, the speed with which they can be deployed, and their ability to support the grid. Here we compare their sustainability in terms of storage efficiency and capacity, safety, use of scarce resources, and impacts through all stages of their lifecycle.
Storage efficiency and capacity
For both batteries and pumped hydro, some electricity is lost when charging and discharging the stored energy. The round-trip efficiency of both technologies is usually around 75% to 80%. This level of efficiency for either technology represents a significant displacement of non-renewable generation if we assume that the stored generation would not otherwise occur.
A particular consideration for batteries is degradation. Batteries degrade as they age, which decreases the amount they can store. The expected life of the batteries that will be used for the recently announced battery storage project in South Australia is about 15 years (depending on how the batteries are operated). By the end of that time, the capacity of the batteries is expected to have dropped to less than 70% of their original capacity.
To maintain a reliable and steady capacity for storage as batteries age and degrade, large-scale battery plants will require ongoing staged installation and replacement of batteries. In comparison, the degradation of pumped storage is close to zero. With appropriate maintenance, peak output can be sustained indefinitely.
Safety
No storage solution can be considered sustainable unless it is safe. The greatest risk relating to pumped storage is dam safety. If it occurs, dam failure can affect downstream communities and the environment, with its impact potential likely to be far greater than a battery safety incident. Nevertheless, pumped hydro technology is mature, dam risks are generally well understood and managed, and the frequency of dam safety events is low.
The main safety concern for batteries is thermal runaway leading to explosions and fires. The severity of this risk will depend on how a battery project is implemented. In a modular arrangement, thermal runaway would be localised, not affecting the whole bank. However, because of the very rapid deployment of evolving battery technologies, safety standards may not be rigorously enforced.
Impacts on land and water
Pumped hydro and grid-scale battery plants may have environmental and land-use impacts. These impacts would vary depending on the sensitivity of the site selected.
A grid-scale battery facility needs a relatively small parcel of land and is likely to be able to be created very close to the energy demand or where generation occurs. Land in these areas has often already been disturbed and the new operations may have little extra environmental impact. Land and water impacts of batteries relate more to their disposal at the end of their effective life, and to the extraction of the resources to produce new batteries.

Pumped hydro requires a relatively larger parcel of land with a very particular topography, and may be far from the location of the demand. Any potential environmental impacts associated with construction and operation need to be considered and mitigated, including those immediately associated with the site, as well as downstream.
In most construction of new pumped hydro, sites are selected where impacts can be mitigated to acceptable levels, for example by using existing reservoirs, or locating ‘closed loop’ systems away from rivers. Although these arrangements will have lower overall impacts, some environmental challenges may still occur during construction when existing water is removed from the site as well as finding a source of water without impacting the environment and other users.
Environmental impacts during operation of pumped hydro are minimal. However, the ecology within the reservoirs will need to adapt to frequently changing water levels, reducing diversity in the system especially within fringing communities.
In all pumped hydro systems, water is re-used over and over again, extracting maximum value from the resource. Nevertheless, depending on the configuration of the pumped hydro project, there may be an ongoing demand for water to top up the storages to counter evaporation.
Minerals and materials
Batteries and pumped hydro require a range of different resources and materials. Lithium-ion batteries use common materials such as plastic and steel as well as chemicals and minerals such as lithium, graphite, nickel and cobalt. Although pumped hydro mainly relies on common building materials such as concrete and steel, the quantities of these materials and the construction impacts can be significant.

Image courtesy of Greensmith, a Wärtsilä Energy Solutions company.
Determining the ultimate sustainability of the required resources and materials for both technologies needs to take account of the full lifecycle and supply chain (mining, processing, refining and manufacturing) as well as end-of-life issues such as recycling, disposal or decommissioning.
Currently, the environmental and health impacts of mining are a significant sustainability concern for the battery industry, and impacts are likely to intensify as worldwide demand for the necessary minerals rapidly increases. Short-term availability of many of the necessary minerals for battery development, such as lithium, appears sufficient, yet security of supply could be compromised by geo-political factors, and long-term availability will depend on levels of demand.
Ultimately, the minerals used in lithium-ion batteries are finite resources, so limiting or reducing their extraction (for example, through greater recycling or substitution for another battery technology) would increase longer term sustainability.
End of life
A battery’s life depends on the technology and on frequency of charging and discharging. Once their effective life is up, the batteries must be disposed of and replaced. Disposal of batteries is a problem we’re yet to face, but as large-scale battery storage proliferates, increasing numbers of batteries will enter the global waste stream. Without careful management of disposal, what cannot be recycled may end up in landfill and may be corrosive, flammable, or could leach toxins into soil and water.
The development of cost-effective and efficient battery recycling methods is still in its infancy.
Although most of the components of batteries can be recycled to some extent, recycling is currently expensive and there is insufficient volume to encourage commercial enterprises to take on recycling the new generation of batteries. In time, improved recovery and re-use of materials will certainly increase the sustainability of battery storage, preserving virgin resources and reducing the impacts of extraction and processing.
End-of-life considerations for pumped hydro seem very distant right now due to hydropower’s longevity, but sustainable decommissioning still needs to be planned for, including managing the impacts on the downstream environment if a dam is removed and rehabilitating the reservoir area.
Lifecycle analysis
At this early stage of development of large-scale battery technology, comprehensive lifecycle analysis is limited by the diversity of battery materials and widely different scenarios of charging, battery life and recycling.
In contrast, the full lifecycle of pumped hydro is better understood due to the maturity of the technology. Pumped hydro is not without impacts, but the risks are known and generally manageable. A major advantage of pumped hydro over batteries is that the expected life of pumped hydro is more than 100 years, or effectively unlimited with appropriate maintenance.
Batteries may have a lower upfront cost than pumped hydro and be easier to approve and install; however, they are likely to require greater management over time. If a projection is made based on current information, the full lifecycle cost and impact of batteries may be greater than hydro across the long term, particularly when mining, recycling and disposal are taken into account. Yet, battery technology is likely to improve very rapidly, which would tighten the gap on pumped hydro’s current lifecycle advantage.
A greener grid
Worldwide, increased levels of renewable energy will lead to a greener grid. It is easy to recognise the sustainability benefits of using a storage solution such as pumped hydro or batteries to further enable the decarbonisation of the network through greater uptake of renewable energy. However, the storage solutions that enable more renewables must also be sustainable – not only in the use phase, but also upstream and downstream.
It is difficult to make a straightforward comparison of the sustainability credentials of pumped hydro and battery storage technologies at their very different stages of maturity. As battery technology is still evolving, its overall sustainability is still somewhat uncertain, but this will change with experience and improvements in battery life and recycling. Meanwhile, pumped hydro projects can last up to a century and associated risks are known and can be mitigated.
Either way, as we redevelop the electricity grid, we will also need a mature approach to lifecycle analysis of our storage solutions.
About the authors
Donald Vaughan is Entura’s Technical Director, Power. He has more than 25 years of experience providing advice on regulatory and technical requirements for generators, substations and transmission systems. Donald specialises in the performance of power systems. His experience with generating units, governors and excitation systems provides a helpful perspective on how the physical electrical network behaves and how it can support the transition to a high renewables environment.
Nick West is a civil engineer at Entura with 16 years of experience, primarily in hydraulics and hydropower. Nick’s skills range from the technical analysis of the layout of hydropower projects to the preparation of contractual project documents and computational hydraulic modelling. Nick was a key team member of the Kidston Pumped Storage Project Technical Feasibility Study.
MORE THOUGHT LEADERSHIP ARTICLES
Batteries vs pumped hydro – a place for both?
Two very different storage technologies – one old, one new; one that takes years to build, one that can be built ‘within 100 days (or it’s free)’. How else do they differ, and is there a place for both?

The rapid growth of renewable energy generation has been driven by two concurrent factors: the falling levelised cost of the energy produced by wind and solar, and the retirement of a number of coal-fired power stations. The recently released Finkel Review notes that by 2035, approximately 68 per cent of the current fleet of Australian coal generating plants will have reached 50 years of age.
The Clean Energy Target proposed by Dr Finkel is not yet confirmed but it recommends incentives for technologies with low or zero carbon emissions. More renewable energy generation brings new challenges in an increasingly complex grid. Dr Finkel therefore also proposes that energy storage be mandated for solar and wind farms.
Renewables can’t, on their own, meet the fluctuations in demand that occur throughout the day without some regulation as to when power reaches the grid. Power needs to be dispatchable. Dispatchable means that energy can be provided upon request. If the sun is not shining or the wind is not blowing, renewable energy cannot be dispatched unless it has been stored in some way.
There are a number of different types of storage but the two being discussed most widely right now are batteries and pumped hydro energy storage. These two technologies are very different and there are some limitations involved in comparing a well-known and established technology with one that is new and developing rapidly.
How do they support the network?
Pumped hydro is based on well-established synchronous generation, providing critical ancillary services to the grid, through the provision of inertia, frequency and voltage support and sufficient fault level support.

Battery inverter technologies are still catching up on most of these fronts. The potential for batteries to provide ‘synthetic inertia’ or fast frequency response is high but this is balanced by their reliance on system strength to be able to deliver this support. They offer minimal support with fault levels but can still provide some support to system frequency and voltage regulation.
How fast can they happen?
There’s no doubt that battery storage is quicker to implement than pumped hydro. South Australia has provided an example of just how quickly battery storage can be deployed.
In March 2017, the South Australian Government called for expressions of interest for the supply of grid-connected battery storage to be connected by the end of 2017. The overwhelming response from 90 interested parties tells us that this speed of deployment is within the realms of possibility.

Battery image courtesy of Greensmith, a Wärtsilä Energy Solutions company.
Pumped hydro, by comparison, is a technology that takes much longer to implement. Typically, development activities (including optimising the technical solution, environmental and social assessments, arranging finance and finalising design) take two years or more to complete, and construction takes another two to three years.
How do the capital costs compare?
Pumped hydro boasts a very low price per megawatt hour, ranging from about $200/MWh to $260/MWh. Currently, battery costs range from $350/MWh to nearly $1000/MWh, with this cost reducing rapidly (costs reduced by about 25% during 2016).
According to the Lazard’s Levelized Cost Of Storage report, capital costs for pumped storage projects around the world range from about $1.5 million to $2.5 million per MW installed. The report also reveals that the cost of installing a grid-scale battery solution ranges from about $3.5 million to $7.5 million. This wide range of pricing for batteries is typical of a developing technology that is implemented in a variety of applications.
Ultimately, it’s difficult to predict how low the cost of batteries may go, but reports predict costs of lithium-ion batteries at somewhere around $120/MWh by 2025.
Considering that batteries need to be replaced once or twice a decade, with the currently available technologies, a battery facility will need to be replaced a number of times during the potential 100-year life of a pumped storage project. For batteries, assuming an economic life of 40 years, the initial cost plus replacements may mean whole-of-life costs fall in the range of $200/MWh to $330/MWh.
So, what does the future hold?
The rise of renewables will inevitably lead to a diversity of storage and supply solutions. The range of these solutions will depend on the resources of particular regions and locations. It is highly likely that the future for both batteries and pumped storage technologies will be extremely bright.
Batteries are here to stay and will undoubtedly play a significant role in future power systems as the technology develops and costs fall. However, while batteries can provide fast response times, they are yet to demonstrate their ability to provide the full range of ancillary services needed to support the grid. Pumped hydro remains a landmark, proven and reliable technology, able to meet the needs of the grid and provide sustained output for up to a century.
Ultimately, there is room for both batteries and pumped storage hydro, and they may even complement each other. Batteries are more cost-effective at delivering small amounts of stored energy over a short time at high power levels. Pumped storage is more cost-effective at storing and releasing larger amounts of stored energy. Achieving the optimum storage solution will depend on careful planning and finding the best fit for the particular circumstances.
What is certain is that both technologies will play important roles in the development and expansion of a network powered by renewable energy.
If you would like to discuss how Entura can help you with your next utility-scale battery or pumped hydro project, please contact Donald Vaughan on +61 3 6245 4279 or Nick West on +61 408 952 315.
A version of this article was first published in RenewEconomy.
About the authors
Donald Vaughan is Entura’s Technical Director, Power. He has more than 25 years of experience providing advice on regulatory and technical requirements for generators, substations and transmission systems. Donald specialises in the performance of power systems. His experience with generating units, governors and excitation systems provides a helpful perspective on how the physical electrical network behaves and how it can support the transition to a high renewables environment.
Nick West is a civil engineer at Entura with 16 years of experience, primarily in hydraulics and hydropower. Nick’s skills range from the technical analysis of the layout of hydropower projects to the preparation of contractual project documents and computational hydraulic modelling. Nick was a key team member of the Kidston Pumped Storage Project Technical Feasibility Study.
MORE THOUGHT LEADERSHIP ARTICLES
Overcoming the barriers to pumped storage hydropower
With energy reliability a hot topic in Australia, eyes are now turning to pumped storage hydropower… but what has been holding it back?

There are only three pumped storage hydropower projects in Australia, with the most recent completed more than thirty years ago. This is despite the ability of pumped storage hydropower projects to provide the large-scale storage that would complement increasing levels of renewable energy. Why is this, and what are the barriers to developing more Australian pumped storage hydropower projects?
Around the world, pumped storage hydropower projects make up the vast majority of grid energy storage and have traditionally been used by energy utilities to supply additional power to a grid during times of highest demand.
As part of a portfolio of power stations, a utility might operate a pumped storage project infrequently only, if the cost of pumping the water back to the upper storage exceeds the revenue that can be generated from its release.
The main issue facing developers trying to prove the viability of a new pumped storage project is that a sufficient price differential is required to pay for the pumping and to account for the efficiency losses in transmission, pumping and generation. The generation price needs to be sufficiently higher than the pumping price just to repay the variable pumping costs. To repay the heavy capital investment, a margin is required over and above the break-even cost of pumping. This is particularly true where proposed developments are ‘stand-alone’ and cannot be optimised as part of a corporate generation portfolio.
In recent years, electricity price spikes have been irregular with few occurrences each year. Due to the significant capital costs, a pumped storage scheme would require a certain number of pumping/generation cycles at high or maximum pricing to pay a return on investment. These price spikes are unpredictable, so building a business case around these events is risky.
Historically, the daily fluctuation of power prices has not been sufficient or regular enough to attract pumped storage developers. This is beginning to change with increasing penetration of renewable energy leading to an increase in both low and high price periods. More frequent, sustained periods of hot weather (as predicted by climate change models) will also drive up demand for power and therefore the market price.
In the last few months, volatility has greatly increased, creating a greater differential between baseload and peak pricing. This will increase the viability of pumped storage schemes, although the unpredictability and challenges of financing capital intensive assets will remain.
But, even when the economics are right, there are still some other barriers that proponents of pumped storage projects need to overcome:
Finding the right site
Pumped storage projects require significant capital for development. Minimising the cost of construction and operation is key to the successful development of a project. Choosing the right location is a matter of identifying a site with ideal topography, a source of water and good proximity to and location within the transmission network.
A wealth of information is available that is relevant to identifying potential pumped storage hydropower sites. Concept studies for pumped storage hydropower sites can screen potential sites quickly and offer developers greater insight into possible opportunities.
Negotiating access to appropriate sites for pumped storage
While a pumped storage project generally has a significantly smaller footprint than a traditional hydropower project, the features of natural topography that are ideal for pumped storage – high, steep hillsides or cliffs – tend also to be places of great natural beauty and are often designated as reserves, are expensive private land, or have high environmental or social value.
State governments can assist here through streamlined planning and approvals processes for infrastructure developments. This can make sure that the challenges of developing sites do not become insurmountable for developers.
Perceived environmental impacts
Pumped storage projects can occupy many square kilometres and also require transmission lines to connect to the electricity market. Like traditional hydropower projects, pumped storage projects need to attend to environmental issues associated with the project. Environmental impacts for pumped storage projects are assessed in the same manner as for all infrastructure developments.
If the impacts of a project can be mitigated to the satisfaction of the relevant regulatory body and international Standards (such as the International Hydropower Association and International Finance Corporation), a pumped storage hydropower project should face no greater hurdle than any other infrastructure project in this respect.
A pumped storage project may also have to deal with the perception that it uses carbon-intensive thermal power to pump water during the pumping cycle. This may be true unless there is a surplus of renewable energy available, in which case the pumped storage project could be seen to be using this excess renewable energy for pumping. As renewable energy penetration grows, the opportunities for storing surplus renewable energy will increase.
An unfavourable regulatory framework
Inconsistent and uncertain policy positions of the major political parties at both federal and state levels reduce confidence in the energy industry, which deters investment. With debate raging over energy security, a bipartisan view on energy policy, which transcends party politics and the electoral cycle, is urgently needed.
Existing mechanisms are in place to support the renewable energy industry. The Renewable Energy Target (RET) promotes investment in renewable energy projects; however, pumped storage is specifically excluded from the RET where the energy used for pumping exceeds the energy generated. Current policy would have to be amended or complementary legislation enacted in order to reward large-scale storage for the service it provides.
Such changes could include market mechanisms for large-scale storage that could offer incentives for providing inertia and ancillary services from storage at times of peak demand as well as power. Another possible change could be to ensure that large-scale storage asset owners are not penalised under the RET for energy used in the pumping process. This would encourage the development of energy storage as a complement to the growth of renewable energy.
High cost of development activities
The long lead times and high development costs of pumped storage projects are major deterrents to developers. Projects generally take more than 4 to 5 years from the point of conception to ‘power on’, and require millions of dollars of capital for development and hundreds of millions for construction. In other words, when funding is first committed, it may not see a return for five years or more.
In an effort to overcome this barrier, the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) has indicated it will allocate at least $20 million to finance the accelerated development of flexible capacity and large-scale storage projects. The Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC) has also committed to provide successful ARENA funding recipients with the opportunity to secure long-term debt finance to support their projects.
With an increasing interest and emphasis on storage in a power system that is becoming increasingly unreliable (e.g. load shedding in South Australia and lack of reserve events in New South Wales), and with finance from ARENA and CEFC for large-scale storage, the barriers to pumped storage development are gradually diminishing. This action can’t come soon enough for residents suffering through blackouts on days over 40°C.
If you would like to discuss how Entura can help you overcome the barriers for a pumped storage hydropower project, please contact Patrick Pease, Nick West on +61 408 952 315, or Richard Herweynen on +61 3 6245 4130.
A version of this article has been previously published as an op-ed in the Adelaide Advertiser.
About the authors
Nick West is a civil engineer at Entura with 16 years of experience, primarily in hydraulics and hydropower. Nick’s skills range from the technical analysis of the layout of hydropower projects to the preparation of contractual project documents and computational hydraulic modelling. Nick was a key team member of the Kidston Pumped Storage Project Technical Feasibility Study and was involved throughout the development and construction of the Neusberg Hydroelectric Project in South Africa. Nick has successfully completed projects ranging from hydraulic design for small residential developments to the feasibility study of a cascade of four large hydroelectric projects in Malaysia.
Richard Herweynen is Entura’s Technical Director, Water. Richard has three decades of experience in dam and hydropower engineering, and has worked throughout the Indo-Pacific region on both dam and hydropower projects, covering all aspects including investigations, feasibility studies, detailed design, construction liaison, operation and maintenance and risk assessment for both new and existing projects. Richard has been part of a number of recent expert review panels for major water projects. He participated in the ANCOLD working group for concrete gravity dams and is the Chairman of the ICOLD technical committee on engineering activities in the planning process for water resources projects. Richard has won many engineering excellence and innovation awards (including Engineers Australia’s Professional Engineer of the Year 2012 – Tasmanian Division), and has published more than 30 technical papers on dam engineering.
MORE THOUGHT LEADERSHIP ARTICLES
Planning a renewable energy journey in the Pacific
Like many stories of island journeys, the pursuit of high levels of renewable energy in the Pacific involves good planning and skilled navigation to stay safe and on course, and holds the promise of rich rewards.

Throughout the Pacific, island communities are embracing ambitious renewable energy targets , many as high as 100% renewables over the next decade or two. This isn’t surprising, given that these islands are already experiencing significant impacts of climate change, and recognise the environmental benefits of reducing or replacing carbon-intensive diesel power generation.
There are also sound economic benefits to reducing reliance on expensive diesel fuel, which remains the single largest expense to generate power in these remote locations.
The answer to meeting targets, while also reducing carbon emissions and costs, lies in power systems that use only renewable energy. However, transitioning to higher levels of renewable energy in power systems requires confidence that the renewables can provide the energy security, self-sufficiency and system stability required by these remote communities.
Renewable energy technologies may pose some challenges for reliability and quality of power supply, but remedies can be found in enabling technologies. In an isolated power system, matching the renewable technologies with the right enabling technologies at the right moment needs detailed planning.
Every journey needs a map
As each island community’s renewable energy journey is different, careful strategic planning is needed to choose the right solution, to integrate it in the right way, and to be able to scale it up effectively to meet increasing renewable targets and electricity demands.
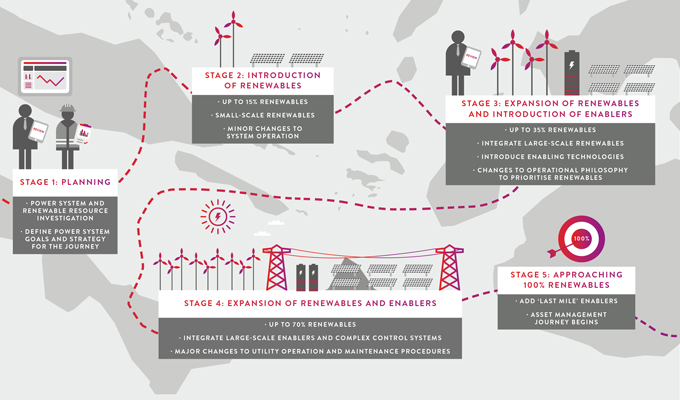
Entura has been helping a number of Pacific island communities embark on their renewable energy journeys. Through this experience, we’ve developed a map of the key stages of the journey:
Stage 1: Planning – In this stage, we explore the status of the current power generation assets, determine what needs to be improved, understand the renewable resource, and investigate the cost of the renewable energy journey and options for funding it.
Stage 2: Introduction of renewables – In this stage, we begin by harvesting the ‘low-hanging fruit’ – introducing the renewables that we can without enablers or network upgrades, and without changing the control philosophy. At this stage, the renewables are perceived as mostly load offset, and could reach up to 15–20% of the island’s total energy demand. Few enabling technologies are necessary at this stage.
Stage 3: Expansion of renewables and introduction of enablers – As we progress beyond 15 to 20% renewable penetration, we need to stop, review and adjust course if necessary. To progress towards 35% renewable energy contribution to the power system demand, we need to adjust the system’s operating philosophy to integrate large-scale renewables, and introduce the appropriate enabling technologies.
Stage 4: Expansion of renewables and enablers – This stage marks the largest change in how an island power system is operated. As we move beyond 50% renewables, again we should stop, review and adjust course where needed. At this stage, power systems become very complex to operate and maintain as high renewable penetration can only be achieved through a delicate balance of multiple new enabling technologies working in perfect sync. The island community could find itself investing more in enabling technologies than in renewable energy at this stage, but this could result in a higher renewable energy contribution. It is also crucial at this point to consider changes to energy delivery, relationships with customers and to the utility’s procedures, and to building its personnel capabilities.
Stage 5: Approaching 100% renewables – As most of the major changes to the power system are introduced in the earlier stages, Stage 5 is about finishing off the journey. The ‘last renewable mile’ is usually the most expensive one, so this last stage is all about identifying enabling technologies and techniques that can bridge the gap between 70–80% and 100% renewable contribution, without significant increases in the cost of electricity.
Yap’s journey to 25% renewables

Entura has helped several island communities plan and begin their renewable journeys. One example is the island of Yap in the North Pacific.
We’ve been working with the Yap State Public Service Corporation to reduce Yap’s heavy reliance on imported diesel for power generation, and to enable the island to rely as much as possible on indigenous, renewable resources through an integrated high-penetration renewable energy remote area power system (RAPS).
After decades of operating on diesel fuel only, the system will soon reach 25% renewable energy contribution. Once completed, the project aims to enable Yap to experience up to 70% instantaneous renewable penetration when conditions allow, and to deliver an annual fuel saving of up to US$500 000.
Back in 2014, Entura helped the Yap community plan their renewable journey by embarking on Stage 1. Since then, Entura has helped the Yap utility to reach Stage 2 by integrating small amounts of solar and by building its capability to install and maintain solar arrays.
The Yap renewable energy development project is now entering Stage 3, in which a new breed of high-renewable-supporting diesel generators are being installed, major works are being carried out to install three 275 kW cyclone-proof wind turbines, an island-wide solar-controlling communications network for 500 kW distributed solar PV is being rolled out, and a centralised control system is being installed.
Once these activities are completed, the Yap power system will be firmly in Stage 3, and ready for future stages in Yap’s renewable journey.
On course for 100% renewables in the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is a group of 15 small islands in the South Pacific, to the north-east of New Zealand. Entura is helping the Cook Islands on its journey to reduce reliance on diesel fuel and achieve greater energy security, self-sufficiency and sustainability through developing renewable power systems on six islands. The country’s goal is to generate electricity from renewable energy sources on all islands by 2020.
The islands of Mauke, Mitiaro, Mangaia and Atiu have small average loads of around 100kW each. After careful planning, upgrades to the distribution grid and programs to train and build local capacity, these islands will quickly reach Stage 5 of their journeys, operating at almost 100% renewable energy using solar PV and batteries, with diesel providing backup during longer periods of renewable energy resource deficiency.

A fifth island, Aitutaki, is currently at Stage 1, finalising the planning of its renewable journey. It will rapidly jump to Stage 3 as 1 MW of solar PV, a 0.5 MW power battery, new diesel generator and centralised control system start working together to deliver a power system with a renewable contribution of up to 25%.
Rarotonga is the largest, main island in the Cook Islands and operates a complex power system requiring meticulous strategic planning. This power system is already at Stage 2, with a renewable contribution surpassing 10% due to the contribution of residential and commercial solar. Entura is helping the Rarotongan utility to move towards Stage 3 by introducing an additional 1 MW of solar PV and enabling technologies such as energy storage, which will help the system absorb even more renewable energy.
The journey continues
It is often said that the end of one journey is the beginning of another. After a community has reached 100% renewable energy, it needs to continue its journey to maintain that status through proper operation, maintenance and asset management, to secure the system for years to come. This long-term asset management challenge involves attention to both physical and human assets, including capacity building, training and skills development for individuals and organisations.
Entura is bringing practical maintenance know-how to island communities such as Yap and the Cook Islands. And, through the Entura clean energy and water institute, we are helping to boost the skills of technicians and managers. By doing so, Entura is offering island communities a guiding hand from the start of the renewable journey right through to its destination, and beyond.
If you would like to discuss how Entura can support your renewable energy journey, please contact Silke Schwartz on +61 407 886 872 or Shekhar Prince on +61 412 402 110.
A version of this article has been previously published by RenewableEnergyWorld.com
MORE THOUGHT LEADERSHIP ARTICLES
Is pumped storage hydro the key to increasing renewables in Australia?
Recent electricity price spikes and a state-wide blackout in South Australia have highlighted the need for reliable power to balance the potential volatility of some renewable power sources.

Pumped storage hydropower projects are a natural fit in an energy market with high penetration of renewable energy as they help to maximise the use of the renewables that are subject to the vagaries of the weather. Pumped storage provides a load when the wind is blowing and the sun is shining, and it also provides a reliable and immediate source of energy when the sun has set and the wind has dropped.
The recent completion of the feasibility study for Genex Power’s Kidston Pumped Storage Hydro Project in North Queensland shows this approach is now technically and commercially feasible.
Pumped storage hydro offers utility-scale storage and system stability
As the proportion of renewable energy in an energy market increases, the need grows for the stability and consistency provided by utility-scale energy storage. For example, South Australia needs system-wide storage of 500 MW for a period of 10 hours to improve the flexibility of wind farm operators, according to the Melbourne Energy Institute.
At the smaller scale of energy storage, the buzz about various types of batteries continues – but the only storage option with a proven track record at the utility scale is pumped storage hydropower.
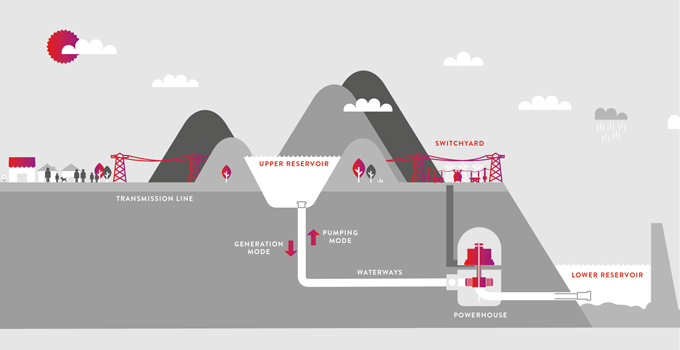
Pumped storage hydropower works by pumping the water stored in a lower reservoir into a more elevated reservoir. The water stored at height can be passed through a turbine on its path back to the lower reservoir, creating electricity as and when needed, and making the best use of the water resource without waste.
In a recent article, my colleague Donald Vaughan stated that a functioning AC power system needs inertia, fault level, frequency and voltage control as well as energy sources to function to an acceptable standard. Pumped-storage assets can provide all of these important contributions to a stable and successful power system, levelling out the fluctuations in availability of wind and solar energy, and helping to regulate voltage and frequency.
New opportunities for pumped storage hydro in Australia
Despite the significant potential and benefits of pumped storage hydro projects, only three projects currently exist in Australia (two in New South Wales and one in Queensland). These schemes were built in markets in which generation was mainly thermal, where the pumped storage could supplement supply at times of peak demand.
A number of possible sites have been identified for new opportunities for pumped storage hydro, but so far very few have been developed beyond concept level. This means that opportunities exist for developers in states such as South Australia and Queensland that have set ambitious renewables targets and must maintain energy security.
Three factors for pumped storage hydro success
For successful pumped storage hydro projects, developers need to identify a viable site, achieve a technically and commercially feasible design, and make the most of the economics of the energy market.
1 – Identifying a viable site
For a pumped storage project, what’s needed is a source of water, and two reservoirs separated by a significant change in elevation. The water could come from a nearby river, an existing reservoir, or the sea. With many thousands of potential sites across the country, a developer needs smart methods of filtering to reduce the many possibilities to just a few ideal sites.
An important consideration is the effect on the viability of pumped storage projects of the relative remoteness of sites, through both the efficiency of the power’s round trip and the marginal loss factors (factors applied to a generator or a load, and calculated based on the size and distance of the generator or load from a central point).
As for any development, the process of identifying sites must also consider topography, land use and environmental constraints. Pumped storage projects generally present similar but reduced environmental risks as conventional hydropower projects as they tend to have smaller footprints.
2 – Achieving a technically and commercially feasible design
Entura’s experience on Genex Power’s Kidston pumped storage hydro project has shown that it is possible to construct low-cost pumped storage projects in Australia through careful site identification and clever project design. Where a pair of suitable reservoirs don’t already exist, constructing a turkey’s nest dam may offer a solution.
A turkey’s nest dam is a reservoir built by excavating earth from the centre of the reservoir and moving it to the edge to help form a continuous embankment. Turkey’s nest dams have been used successfully around the world in pumped storage hydropower projects, providing opportunities to build projects where elevation changes significantly over a short distance.
Additionally, turkey’s nest dams can help to minimise capital costs by reducing conduit lengths and maximising head (the difference in elevation between the upper and lower reservoirs).
3 – Making the most of the economics of the energy market
Understanding the opportunities and constraints in the energy market is critical to a pumped storage project’s financial viability.
When you can store energy, you can dispatch electricity at peak times, gaining the highest price point in the market. Conversely, water is pumped to the upper reservoir in off-peak periods or when supply from renewable sources is high and market prices are low. This ‘energy arbitrage’ makes the most of the price difference in the electricity market.
Selecting the optimum installed capacity of a pumped storage project also requires detailed understanding of energy markets. It is possible that a pumped storage project can act to flatten peak prices to the point where the returns on a project are insufficient to meet financiers’ hurdles, so detailed revenue modelling is essential to determine the tipping point between enough and too much installed capacity.
With careful selection of sites, clever design, and the right mix of capacity and costs, pumped storage hydro holds an important key to unlocking the full potential of renewables in Australia’s electricity market.
If you would like to discuss how Entura can help you explore potential opportunities for pumped storage hydropower projects, please contact Nick West on +61 408 952 315 or Richard Herweynen on +61 3 6245 4130.
About the author
Nick West is a civil engineer at Entura with 15 years’ experience, primarily in hydraulics and hydropower. Nick’s skills range from the technical analysis of the layout of hydropower projects to the preparation of contractual project documents and computational hydraulic modelling. Nick was a key team member of the Kidston Pumped Storage Project Technical Feasibility Study and was involved throughout the recently completed Neusberg Hydroelectric Project in South Africa. Nick has successfully completed projects ranging from hydraulic design for small residential developments to the feasibility study of a cascade of four large hydroelectric projects in Malaysia.
MORE THOUGHT LEADERSHIP ARTICLES
Eight principles for successful investment in renewable energy projects
When you are considering investing in a renewable energy project, a thorough due diligence investigation can identify the costs, benefits and risks, and lead to well-informed decisions.
In practical terms, this is about asking the right questions about the project, distinguishing when an issue is important and when it is not, and prioritising your efforts.
Why prioritise your efforts? Because the unfortunate reality is that most due diligence investigations don’t result in an investment. As consultants, we are aware of this reality, but as part of a larger business that acquires, develops and owns renewable energy assets, we understand that effort and expenditure must produce results.
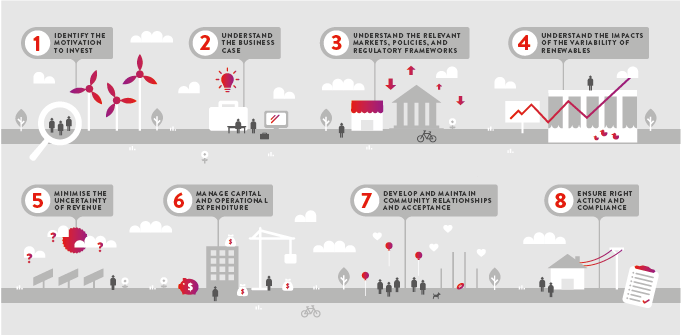
When we lead renewable energy due diligence investigations, we often start with a quick assessment to establish as soon as possible if there are any ‘show stoppers’. No matter how preliminary or comprehensive the assessment, these eight principles guide our considerations:
1 – Identify the motivation to invest
A thorough due diligence investigation will identify high-level issues such as sovereign risk, right down to detailed technical issues associated with the particular investment opportunity.
Your motivations as the investor will influence the assessment of these risks. It may not simply be all about financial return, but also a desire to limit carbon exposure or to increase corporate social responsibility. And if we understand your business, we can bring a clearer perspective to the assessment.
Traditionally, investors have relied on consultants to assess the technical issues in detail, but have preferred to assess high-level risks ‘in-house’. This approach is understandable, but it may not be making the most of your consultant’s knowledge. Most renewable energy consultants these days have been in the game a long time, and you will find them keen to provide a more holistic assessment of risk.
2 – Understand the business case
As with any investment decision, investors interested in renewable energy projects need to understand the level of investment of financial and human resources required for the project, and the likely returns for that investment – the business case.
Each project will have its own set of issues and risks to identify and potentially mitigate as part of a robust business case. Risks will affect the revenue stream, the cost of the project, and/or the social acceptability of the project.
An experienced due diligence provider can provide value by recognising the difference between issues that will materially affect the project business case and those that will not, or by identifying opportunities where others might only see risks.
3 – Understand the relevant markets, policies and regulatory frameworks
Renewable energy projects are often supported by government policies that recognise the environmental benefits of clean generation and support the revenue stream for the project. It is essential to understand both the commercial market for your energy and this policy environment.
You also need to understand the relevant regulatory frameworks – planning, environmental, electricity grid, corporate governance, taxation, financial, employment, or occupational health and safety. All these factors need to be considered when assessing the cost of the project and the risks associated with the investment.
4 – Understand the impacts of the variability of renewables
Renewable resources such as solar, wind or small run-of-river hydropower schemes generate power with a variable output that can be forecast, but is not necessarily available on demand. This feature of renewable energy can lead to quarterly or annual variations in generation and in revenue that are beyond the control of the owner.
However, renewable projects do not have variable fuel costs. So by weathering the short-term fluctuations of renewable generation through prudent technical and financial risk management, you can achieve greater long-term certainty in your business case than with non-renewable generation projects.
The variability also means that when the resource is available (for example, the sun is shining), you want your project to export energy to the electricity grid without constraint. Therefore, for renewable energy projects, the grid connection arrangements can mean the success or failure of your project.
5 – Minimise uncertainty of revenue
The variable nature of renewable generation can create short-term uncertainty in revenue; however, long-term certainty in revenue is generally a must-have for a renewable energy project looking to sell its power output.
In some markets, set tariffs may be offered from government bodies for renewable projects. In markets with a floating electricity price, long-term power purchase agreements are often sought with counterparties such as retailers or large-scale energy consumers.
There may not be much assistance a consultant can provide on this issue – except to remind you to read the fine print of any agreements and, if the project does not have a confirmed buyer for the power, make sure you know the risks!
In terms of what the project is technically capable of generating, an operational project has more certainty than a development site, and may be more attractive for some investors.
6 – Manage capital and operational expenditure
Renewable energy projects require a large upfront capital expenditure. Depending on your risk appetite as an investor, exposure to risk can be managed through the contractual arrangements with the developer, equipment suppliers and the construction contractor. Comprehensive long-term operations and maintenance agreements are often available, which reduce your risk, but at a cost.
One issue worthy of particular note is construction delays. Investments that are otherwise sound can suffer due to delays in construction, which can have significant impacts on the expenditure and revenue profiles, and the terms of any debt provision.
7 – Develop and maintain community relationships and acceptance
Renewable energy projects operate within communities. There will be a range of attitudes towards your project and relationships to manage, and it will be up to you to develop and maintain a healthy relationship with the community.
Your community may see your project as a major contributor to the local economy through direct employment and indirectly through contracting. The community may even expect you to play a leading role in supporting local community activities through sponsorship and other activities.
8 – Ensure right action and compliance
An opportunity to invest in a renewable energy project might occur at any stage of the project. Regardless, the nature of the due diligence is usually very similar – have the right actions have been undertaken, does the project comply with its commitments, and will it continue to comply into the future?
Because Entura is part of Hydro Tasmania, Australia’s largest renewable energy producer, we understand what it means to live with the full consequences of investment decisions and risks. So we approach due diligence for our clients in the same way we would if the investment opportunity was our own.
That means developing a full understanding of the proposed project, discovering any risks that could prevent its success, and finding the best ways to make the most of the project’s strengths and avoid any possible weaknesses.
If you are seeking to invest in renewable energy, Entura can assist you with practical, expert due diligence services for proposed or operational projects in the Asia-Pacific region. Please contact Patrick Pease or Silke Schwartz on +61 407 886 872.
About the author
Seth Langford is a specialist renewable energy engineer at Entura and has been working in the wind industry for more than ten years. Seth has been involved with major wind farm projects as a technical specialist and a team leader for feasibility studies and due diligence projects in India, China, Australia, Sri Lanka, South Africa and New Zealand. Seth has spent considerable time assessing greenfield and operational wind farms on behalf of developers wishing to acquire wind farm projects.
MORE THOUGHT LEADERSHIP ARTICLES
A bright future for RAPS: reliable, cheaper power for remote areas
Remote area power systems that integrate renewable energy sources such as solar and wind with storage or diesel backup are increasingly allowing remote communities to become more self-sufficient and sustainable by providing dependable, secure power that is cheaper than relying on diesel-generated power alone.
Saving money and the environment
Using renewable energy technologies to create power in a range of remote areas such as small to medium towns, mines or even islands makes perfect sense. The fuel usually used in these locations is diesel, which is expensive, vulnerable to broader pressures on price and supply, and can also be slow, complicated and costly to transport to remote areas.
Falling costs of renewable technologies, free fuel from the sun and wind and large savings on displaced diesel add up to significant commercial motivation to move towards renewable or hybrid systems. But there’s also a compelling environmental argument for developing RAPS – it reduces consumption of fossil fuel, lowers carbon emissions and helps reach sustainability goals.
This environmental argument carries extra urgency for low-lying island communities on the front line of climate change, as rising sea levels threaten their very existence.
Why Yap needs RAPS
To the north of Papua New Guinea, in the Western Pacific Ocean, lies one of these vulnerable islands: the postcard-perfect paradise of Yap. While Yap has already started to recognise the early impacts of climate change and increasingly severe weather events on its farms, coral reefs and palm-lined beaches, it has also witnessed at close range the high consequences of vulnerability to oil prices, as the world oil price shock in 2008 threw the neighbouring Marshall Islands into a state of fiscal crisis with the government having to bail out its own state-owned power utility.
As an early step towards reducing Yap’s heavy reliance on imported diesel for power generation, and to enable the island to rely as much as possible on indigenous, renewable resources, the Yap State Public Service Corporation (YSPSC) commissioned specialist power and water consulting firm Entura to design and supervise the delivery of a US$11 million integrated high-penetration renewable energy RAPS.
The RAPS project will also help Yap play its part in helping achieve the Federated States of Micronesia’s ambitious targets of 30 per cent renewable energy by 2020 and 70–100 per cent by 2050. The project will reduce fossil fuel consumption in Yap through developing renewable energy and improving the supply-side energy efficiency of the current grid. Once completed, the project aims to provide 17 per cent of Yap’s annual energy production and enable Yap to experience up to 70 per cent renewable penetration when conditions allow. The system is forecast to deliver an annual fuel saving of up to US$500 000.
Integrating renewables no longer a challenge
Until recently, integration issues have made it difficult to introduce large amounts of renewable energy into remote diesel-based electricity systems. High intermittency of renewable sources presented challenges for reliability and quality of supply in remote power systems. But new technological developments such as intelligent control systems, improved storage technologies and demand-side management assist with overcoming these concerns and increase the reliability of off-grid renewable systems.
As each RAPS is different, the challenge that remains is choosing the right solution and integrating it in the right way.
Yap’s power system is designed to meet the 2.2 MW load for the 7000 people living on the main island, delivering up to 1 MW of wind energy from small but robust turbines and 300 kw of remotely controlled grid-connected solar energy from the rooftops of seven government buildings. Two high-speed diesel generators have been included in the system, and have been selected for their responsiveness and ability to support higher renewable energy penetration and even out any energy fluctuations.
The clever trick to keep all these different electricity-generating assets working together smoothly to provide a continuous and reliable electricity supply is an innovative integration and control system. The overall design of Yap’s integrated high-penetration renewable energy system, combined with the automated integration and control system, balances and maintains the quality of the energy supply to maximise the amount of renewable energy used on the island.
Building capacity for the long term
The YSPSC is a sophisticated utility that fully embraces its commitment to provide clean and affordable power that is sustainable not only for the environment and the economy but also for Yap’s community in the long term.
The power system has been carefully designed to be able to realise future goals of operating at zero diesel, as well as to be able to be operated and maintained within the community rather than by external specialists.
YSPSC and Entura are working together to deliver the principles of ‘design and build, operate and maintain’, as opposed to a ‘build-neglect-rebuild’ paradigm, by working to develop capacity within the Yap community, so that the local people will not only be the owners of a new state-of-the-art energy system, but will also have the opportunity to develop the skills to operate and maintain it into the future.
Construction of the Yap RAPS is due to start in mid-2015 and finish in early 2016.
RAPS around the world
Entura and its parent company, Hydro Tasmania, have previously been involved with the delivery of hybrid off-grid systems and RAPS in the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, King and Cape Barren Islands, and are currently assisting our clients in delivering a suite of projects in Australia, as well as in the Cook Islands.
Hydro Tasmania’s hybrid off-grid solution on King Island is now recognised as a world-first, achieving the ability to operate a megawatt-class power system solely on renewable energy sources for extended periods of time, when conditions allow. The King Island Renewable Energy Integration Project has also demonstrated that hybrid systems with the right mix of enabling and generation technologies are not only lower cost alternatives, but can also be more reliable and robust than traditional diesel generation in off-grid systems.
If you would like to discuss if a RAPS is the best solution to power your remote operations or community in a sustainable and cost-effective manner, please contact Silke Schwartz on +61 407 886 872 or Shekhar Prince on +61 412 402 110.